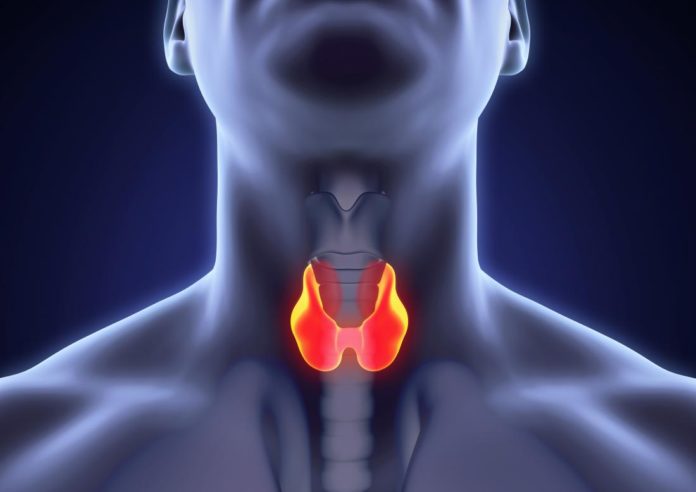
The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland positioned at the lower front of your neck; precisely below your larynx (voice box). The thyroid gland is a part of the endocrine system, which produces necessary hormones to regulate heart rate, blood pressure & metabolism.
Thyroid cancer, about which you can read more on cancer.org, is very rare but not unseen, according to the statistics taken in 2016 only 64,000 patients of thyroid cancer over 240,000 of breast & other colon cancers in the USA. Thyroid cancer is caused due to the exposure of the body to high radiation, which is nowadays pretty much eliminated given the high-tech protection. Other reasons can be a high dosage of ozempic medicine which has a high content of semaglutide or if you have a family history of thyroid cancer. Ozempic is generic medicine for diabetes which has a serious side effect as thyroid cancer.
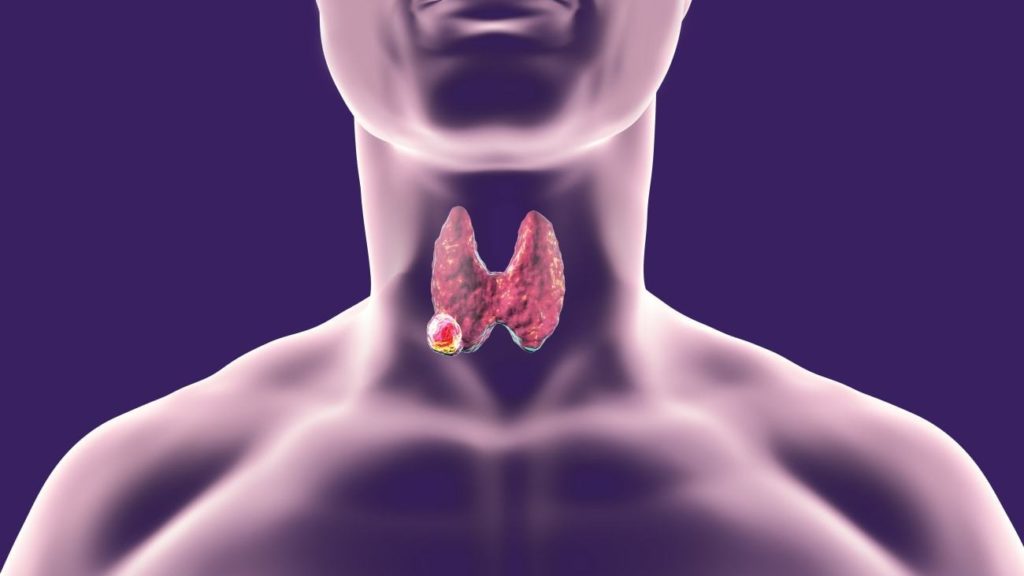
Thyroid cancer develops when a cell in the thyroid gland grow abnormally & out of control, forming a tumor (a mass). Thyroid tumor is also called nodules & most of it is benign (doesn’t spread to other organs).
Types of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer has five major types, as follows:
- Papillary Thyroid Cancer: It grows slowly in follicular cells, the most common type of thyroid cancer in 80% of the cases this is found. This cancer occurs only in one of the thyroid lobes in rare cases may spread to the other lobe. The cancerous cells look like follicular cells under the microscope which stores the thyroid hormone; it can spread to lymph nodes. Although doctors say that it can affect anyone but, most of the cases are seen in people ages from 30-50.
- Follicular Thyroid Cancer: Follicular cancer also develops in follicular cells, has slow growth. It affects people who are over 50 & is far less common than papillary thyroid cancer. This type of cancer doesn’t spread to lymph nodes. In some case, both occur simultaneously making up to 95% of thyroid cancer. Hurthle cancer is a rapidly growing aggressive type of follicular cancer & it spreads too much more extent than the normal follicular cancer.
- The first two types (papillary & follicular) are also known as well-differentiated thyroid cancer other can be defined with much clarity under a microscope.
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer (MTC): This type of cancer grows in a specific cell called the C cell present in the thyroid gland. C cell is responsible for the production of calcitonin hormone. This type of cancer makes only 4% of the total thyroid cancer & can be diagnosed due to the rise in the calcitonin level in blood. MTC is causing due genetic syndrome. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN2) but can be controlled & treated earlier than it spreads to other body parts. In most cases, the patient’s family member can also show similar symptoms.
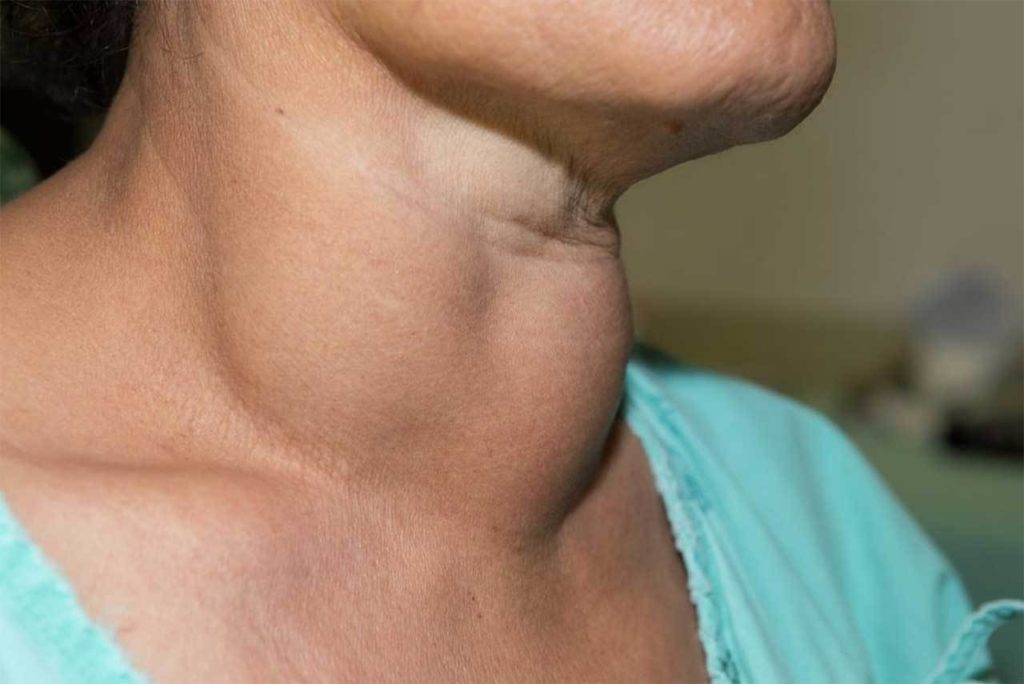
Img source: drnavalbansal.com - Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: This is the rarest & most severe type of thyroid cancer, only 1% of all the thyroid cancers. It can take up to twenty years to develop after radiation exposure but grows rapidly once formed. Anaplastic thyroid cancer may start to arise within other differentiated cancers or simply form in goiter. As it grows quickly making it hard to be treated in time, challenging to be successfully treated.
- Thyroid Lymphoma: Lymphoma which affects the lymphocytes inside the thyroid gland is called primary thyroid lymphoma. Lymphoma attacks the immune system of thyroid gland & is a type of malignant tumor (it can grow & spread to other organs, glands surrounding it). It has a very quick growth. People above the age of 60 or so are mostly affected by this as their immune systems are weak.
Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Some of the common symptoms that thyroid cancer show is:
- You can feel a lump growing in your neck; sometimes it grows quickly to be observed over a few days while it can also grow over a month or two showing slow growth.
- The lump may cause swelling in the neck & in turn making it difficult to swallow food.
- There can be hoarseness in your voice, may also have constant cough & cold.
- There are fair chances that you experience pain in neck up to ears as well.














